| Selections and Masks | |
|---|---|
|
Selections in Photoshop allow you to change only specific parts of an image, while leaving the other areas untouched. Used together with other photo editing techniques, selections and masks give you a fine degree of control.
A selection mask is simply a ring of pixels, usually represented by a moving dotted line. |
|
| Part of | Photoshop CS5 |
| Part Type | Interface |
| Screenshot |

|
Selection Options
The selection tool in the tool bar comprises a variety of ways to select certain areas within an image. To select more than one part of an image while using any of the below methods, you simply need hold SHIFT and continue to select additional areas. This will add the new area to your selection. If you hold ALT and select areas within a selection, those areas will be removing according to the same selection criteria. Understanding how to add and remove parts of your selection will help you to make the best overall selection of any aspect of your base image or images, potentially giving you near pixel perfect selections if you take the time.
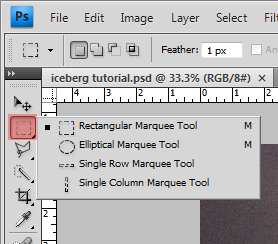
Marquee Selection
The marquee selection tool includes rectangular box selections, elliptical and circular selections, and single row and column selections. These tools are not detail oriented unless your selections are perfectly orthogonal, elliptical or circular. However, if you selecting large, blanket spaces across an image for whatever reason, the rectangular selection tool can come in handy to cover a lot of surface area quickly, such as "
selecting everything on the left side of the page
". The list of marquee tool options that is shown in the above image comes up when you hold the mouse button down on the marquee selection button.
Toolbar Tip : Whenever you have the small triangular tab at the bottom right of any toolbar icon, you can hold your mouse down on it to reveal the additional commands inside of it.
Lasso Selection
All Lasso tools require that for an area be selected, it must be fully encompassed, so the beginning point and end point must touch eventually, creating an enclosed space in between. If you double click your last point, it will automatically snap back to the beginning point to complete the enclosure, creating a straight line in between the points (last and first).
- Freeform Lasso
- Polygonal Lasso
- Magnetic Lasso
The Freeform Lasso
is like drawing a sketchy line around something. It's loose and does not allow for high precision. However, like the rectangular marquee tool, it can help to select pre-cut areas in a layer. Use it like a pencil for highlighting, not a knife for cutting.
The Polygonal Lasso
is an effective way to select small areas that cannot easily be grouped by photoshop into other selection options. Generally, thin pixelated lines are tough to select without the polygon lasso tool, and high-detail spaces look best when cleaned up with the polygon lasso tool.
The Magnetic Lasso finds contrasting edges based on a frequency of sampled points on the image. The detail of the magnetic lasso can be adjusted by changing the frequency (higher is more detailed), while the contrast level can also be adjusted. This tool generally does not work well on right angles, but works quite well on irregular shaped objects. However, you'll need to move slow and be patient. If you make a mistake, you can simply select "delete" to remove the last point in the line.
Quick Selection and Magic Wand Tool
- Quick Selection Tool
- Magic Wand Tool
The Quick Selection Tool
allows you to draw at a specific pixel size all the area that you want to select, automatically finding edges close to where you draw your line. As long as you keep your selection within the boundary you want to stay within, the quick selection tool will seldom veer away from this boundary. By adjusting your pixel size, you can touch up a selection done with quick selection by adding or subtracting from the initial selection.
By default, the quick selection tool adds areas without having to hold shift, and to remove areas, you can select the upper quick selection tool option with a negative sign next to it. However, the standard
SHIFT
for add and
ALT
for remove will still work as well if you're used to using them.
The Magic Wand Tool
is a great way to select areas of similar tone and color. Subtle shade changes are hard to depict with this tool, and better left with other selection options, but when it comes to finding like colors, this tool is the best. It automatically finds the outer most edges that share similar tones and colors according to a tolerance setting in the upper options. A low tolerance will focus on VERY similar pixels, while a high tolerance will incorporate a larger variety of similar colors and tones. Playing around with the tolerance can help you fine tune the magic wand tool for a specific image or area within an image.
Tool Tip : When making complex selections, feel free to save them by clicking "Select>Save Selection". This will allow you to bring up the selection on another layer or the same layer later on without having to take the time to re-select a complicated path.
Quick Masks
The Quick Mask tool uses the paintbrush to paint areas that are either masked or selected. Access the tool by typing "Q", or find the button with an icon of a circle within a rectangle on the toolbar. Or, click Select --> Edit in Quick Mask Mode. To change between the Masked Areas and Selected Areas options, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) the Quick Mask Mode button.
To choose a new mask color, click the color box, and choose a new color. To change the opacity of the color, enter a value between 0% and 100%. Both the color and opacity settings affect only the appearance of the mask and have no effect on how underlying areas are protected. Changing these settings may make the mask more easily visible against the colors in the image.
Masked Areas
Masked areas are black (opaque) and selected areas are painted white (transparent). Painting with black increases the masked area; painting with white increases the selected area. When this option is selected, the Quick Mask button in the toolbox becomes a white circle on a gray background .
Selected Areas
Masked areas are white (transparent) and selected areas are black (opaque). Painting with white increases the masked area; painting with black increases the selected area. When this option is selected, the Quick Mask button in the toolbox becomes a gray circle on a white background.