| Week 8: Orthographic Entourage | |
|---|---|
| Course | Arch 100b |
| Date | 2013/03/15 |
| Learning Objectives | In this session, we will discuss the importance of using entourage in architectural renderings, both in perspective and orthographic representations. We'll focus on how to interpret the relationships of space into the drawing's entourage, the methods used to obtain rendered orthographic drawings, and the tools in Photoshop necessary to complete them. |
| Agenda |
|
| Uses Tool(s) | Photoshop CS5 , Illustrator CS5 |
Orthographic Entourage
Using architectural entourage is the expression of a spatial idea upon a drawing. The composition of all parts of the drawing determine how one reads the scale, light, space, and texture of the building. Where a line drawing is able to inform the reader of spatial separation, program placement, and even construction, the added layer of entourage can communicate beyond those ideas.
As architects, we use entourage – here defined as the surroundings of a building, or the parts of a drawing beyond purely architectural information, i.e., people, animals, plants, textures, shadow, and light – to tell the viewer what that space may be like when inhabited. Though these techniques are typically used in perspective renderings, as many designers feel that it is the most straightforward opportunity to show how a space is experienced, they can also be used with orthographic drawings for a similar effect.
Examples and Inspiration
Tools of Note in Photoshop
Selection Options
The selection tool in the tool bar comprises a variety of ways to select certain areas within an image. Regardless of what selection method you choose below, you can edit what is and is not selected at any time, assuming you haven't locked your layers. To select more than one part of an image while using any of the below methods, you simply need hold SHIFT and continue to select additional areas. This will add the new area to your selection. If you hold ALT and select areas within a selection, those areas will be removing according to the same selection criteria. Understanding how to add and remove parts of your selection will help you to make the best overall selection of any aspect of your base image or images, potentially giving you near pixel perfect selections if you take the time.
Marquee Selection
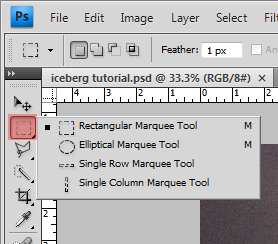
The marquee selection tool includes rectangular box selections, elliptical and circular selections, and single row and column selections. These tools are not detail oriented unless your selections are perfectly orthogonal, elliptical or circular. However, if you selecting large, blanket spaces across an image for whatever reason, the rectangular selection tool can come in handy to cover a lot of surface area quickly, such as "
selecting everything on the left side of the page
". The list of marquee tool options that is shown in the above image comes up when you hold the mouse button down on the marquee selection button.
Toolbar Tip : Whenever you have the small triangular tab at the bottom right of any toolbar icon, you can hold your mouse down on it to reveal the additional commands inside of it.
Lasso Selection
All Lasso tools require that for an area be selected, it must be fully encompassed, so the beginning point and end point must touch eventually, creating an enclosed space in between. If you double click your last point, it will automatically snap back to the beginning point to complete the enclosure, creating a straight line in between the points (last and first).
- Freeform Lasso
- Polygonal Lasso
- Magnetic Lasso
The Freeform Lasso
is like drawing a sketchy line around something. It's loose and does not allow for high precision. However, like the rectangular marquee tool, it can help to select pre-cut areas in a layer. Use it like a pencil for highlighting, not a knife for cutting.
The Polygonal Lasso
is an effective way to select small areas that cannot easily be grouped by photoshop into other selection options. Generally, thin pixelated lines are tough to select without the polygon lasso tool, and high-detail spaces look best when cleaned up with the polygon lasso tool.
The Magnetic Lasso finds contrasting edges based on a frequency of sampled points on the image. The detail of the magnetic lasso can be adjusted by changing the frequency (higher is more detailed), while the contrast level can also be adjusted. This tool generally does not work well on right angles, but works quite well on irregular shaped objects. However, you'll need to move slow and be patient. If you make a mistake, you can simply select "delete" to remove the last point in the line.
Quick Selection and Magic Wand Tool
- Quick Selection Tool
- Magic Wand Tool
The Quick Selection Tool
allows you to draw at a specific pixel size all the area that you want to select, automatically finding edges close to where you draw your line. As long as you keep your selection within the boundary you want to stay within, the quick selection tool will seldom veer away from this boundary. By adjusting your pixel size, you can touch up a selection done with quick selection by adding or subtracting from the initial selection.
By default, the quick selection tool adds areas without having to hold shift, and to remove areas, you can select the upper quick selection tool option with a negative sign next to it. However, the standard
SHIFT
for add and
ALT
for remove will still work as well if you're used to using them.
The Magic Wand Tool
is a great way to select areas of similar tone and color. Subtle shade changes are hard to depict with this tool, and better left with other selection options, but when it comes to finding like colors, this tool is the best. It automatically finds the outer most edges that share similar tones and colors according to a tolerance setting in the upper options. A low tolerance will focus on VERY similar pixels, while a high tolerance will incorporate a larger variety of similar colors and tones. Playing around with the tolerance can help you fine tune the magic wand tool for a specific image or area within an image.
Tool Tip : When making complex selections, feel free to save them by clicking "Select>Save Selection". This will allow you to bring up the selection on another layer or the same layer later on without having to take the time to re-select a complicated path.
Masks and Channels
Layer Masks
Layer Masks are simple ways to view only certain areas within a layer. It allows you to retain the original layer in its entirety while only viewing a part of it. The Black area in the Layer mask is the "hidden" or "protected" part of the mask, while the white area is the "shown" or "revealed" part of the mask. When working with layer masks, we are only working with black (hidden) and white (shown). Layer>Layer Mask
Clipping Masks
Clipping masks are a fast way to clip a layer to a specific area. This works between two layers, where the bottom one is the guide and the above one is the layer that is clipped. The guide layer acts like a layer mask, where all visible parts of the layer are guiding where the above layer will show up. When applying the clipping mask, the guide layer is hidden by the clipped layer above. This works for any irregular shaped selections and works for text too.
I find clipping masks to be the most helpful when you think of it as the bottom layer
drawing in
the top clipped layer. The example of grass below demonstrates this well. You can right click on a layer and select Create Clipping Mask or go to Layer>Create Clipping Mask.
Channels
Channels represent the areas of Red, Green, and Blue in each pixel within your layer. If you select the Red channel, a black and white image will show up that reveals where there is red color information (highest being white and lowest being black). The same applies for the Green and Blue channels, revealing different black and white images when selected. This can help you pinpoint where certain colors are within your layers or overall image. If you save a certain selected area (Select>Save Selection), you'll create an "alpha channel" in the channels menu, which will focus the results to that selection only. Window>Channels
Today's Workflow: Creating an Orthographic Drawing with Shadow and Entourage
This workflow will present the methods necessary to create an intriguing rendered orthographic drawing. After taking an orthographic drawing from Illustrator with proper lineweights, we will add subtle textures and materiality to read the spaces better, add shadow and poche, and finally add people and trees for scale.
Related Workflows
- Rendered Elevations Using VRay and Photoshop
- A rendered section-elevation can depict spatial depth and communicate the design intent of a project in ways beyond a simple utilization of orthographic drawing techniques. Although orthographic drawing may communicate basic technical, material, and spatial qualities through the mechanisms of line and lineweight alone, additional imagistic devices found in raster images can provide for a stronger representation of design intent. This workflow demonstrates how to augment a detailed section-elevation line-drawing with several layers and techniques from VRay and Photoshop as a way of underlying the conceptual basis of a design.
- Creating a Composite Image with the Selection Tool in Photoshop
- This workflow will go through the many ways you can use the selection tool to divide images into separate layers of information that can be edited for specific purposes afterwards.
- Creating Shadows for Plan Drawings
- Shadows on plans help drawings read spatially. This tutorial explains how to edit a shadow render for a plan drawing.
- Section Perspectives From Digital Models
- This workflow will showcase the steps necessary to create a section perspective drawing using a digital model in Rhino. Once the linework is created, we will then export the drawing to Illustrator and finalize the drawing using a variety of fill, opacity and style options to create a presentable drawing.
Today's Exercise: Create a Rendered Orthographic Drawing
Using a given plan drawing, add additional entourage including trees, furniture, material, and people. With the given assets, place entourage in the plan drawing and add shadows and texture. Exercise will measure ability to interpret scale and ability to use tools to create textures and shadow.
Additional Resources
- CG Textures
- Tileable and non-tileable images for many different materials.
- Graphic Addiction
- Blog of student architecture projects models and drawings.
- Drawing Architecture
- Blog of student and professional architectural drawings.
- Immediate Entourage
- Free collection of images of people, plants, textures, and other objects to be used for renderings. Some are of good quality, some are not so great - use discretion.
- Tileables
- Patterns that can be used in Photoshop that are infinitely tileable, including fabrics, woods, and papers. Good for abstract materiality.
- Subtle Patterns
- Used primarily for UI design, these are infinitely tileable images that can be used for adding very subtle textures to drawings. Use responsibly - overuse or inappropriate use will make drawings look unprofessional.